Static vs Dynamic Web Pages
When we send HTTP requests to the web server, the web server responds to the request and sends the page file (usually with a .html extension) back so that we can view the entire web page in the browser. The way the web server processes and generates the web pages categorizes the web pages into static and dynamic.
Static Web Pages
A static web page is a page file stored in the web server. Normally, static web pages are stored with a .html file extension. Each web page has a unique URL (Uniform Resource Locator). When we request a static web page, the web server finds the page file in the file system and sends it back. The server will not do any processing of the page file.

Dynamic Web Pages
The web server responds to dynamic web pages after pre-processing. The dynamic web page is stored in a page file with code. The code instructs the web server to pre-process the page file, generates the corresponding HTML file, and then sends it back to the user.
The pre-processing depends on what code the web server uses. The most common programming language for web server development is PHP. There are other server-side languages such as Python and C#.
We take PhP for example. A dynamic web page written with PhP language is stored in a page file with a .php extension. When we request a dynamic web page, the web server first processes the PHP page file and generates the HTML file. Then the server sends the HTML file back to the user.
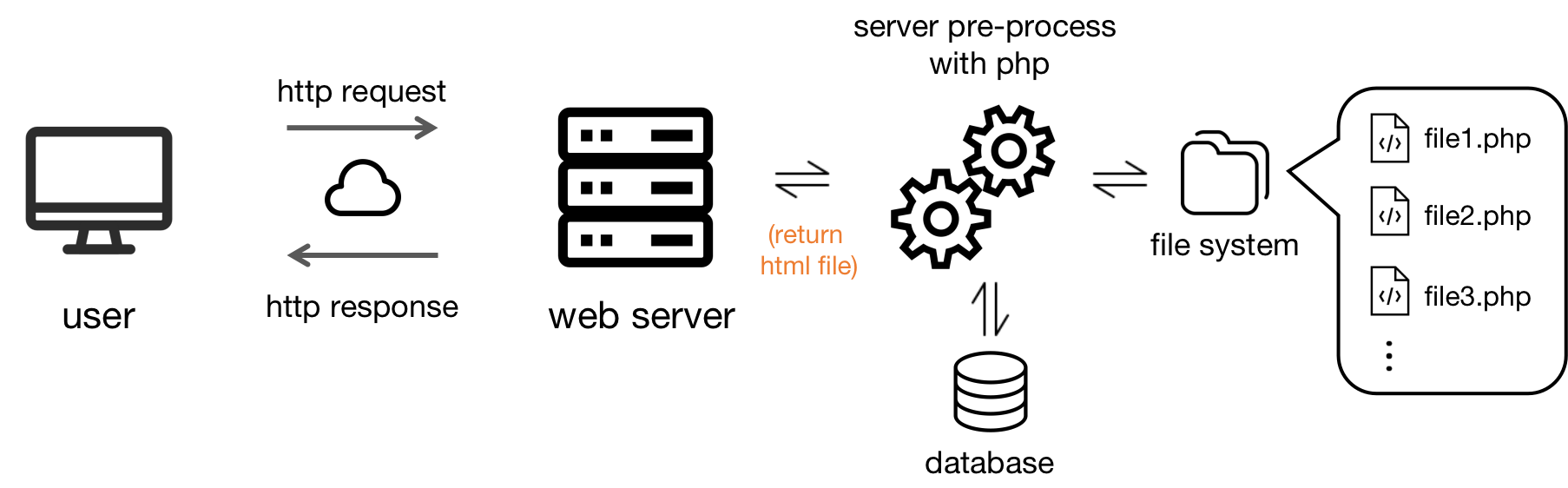
A simple dynamic web page file with PHP looks like this:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<body>
<p>This example shows PHP block and its processed output.</p>
<?php
echo "String Output from PHP Block.";
?>
<p>This PHP code prints addition of two number in the
processed HTML output.</p>
<?php
echo 1+1;
?>
</body>
</html>
Static vs Dynamic
The user can only view the existing page content on a static web page. Therefore, it is more suitable for blogs and news websites. In addition, it is also more secure because the user cannot modify anything on the web page.
A dynamic web page provides more interactions between the user and the website. The code adds more flexibility to the web server to process the web page. It is more suitable for interactive websites such as Google. Let’s consider two examples.
The first example is the stock price query. If we want to check the stock price right now, we request the web server. The web server receives the request and checks the latest database for the stock price. Then the server generates the HTML page file and sends it back. If the stock price web page is static, which means they are pre-generated and stored in the server, we either cannot find the latest stock price, or the web server has to constantly update the page file to ensure the data is in time. Either way, it is not convenient.
The second example is online computing. If we want to perform complex computation, for example, integration, on the web server, we need to input the data first on the website. The web page has to be dynamic. Otherwise, the web server cannot even know what we input on the page. Let along process the input.
Resource
Some useful materials also introduce this topic: